
Inflammation of tissues can cause them to swell, blocking the openings of the pharyngotympanic tubes. When this occurs, it can cause a buildup of fluid that causes Eustachian tube dysfunction. The passages are very narrow, meaning that it doesn’t take much to block them. Sometimes something causes a blockage of the Eustachian tube, preventing it from opening properly.

This mild type of Eustachian tube dysfunction usually resolves itself within a few minutes, although it may also take several hours. For example, some people report mild symptoms from riding in an elevator or taking off in an airplane. It can occur due to changes in air pressure or altitude, especially if these come on suddenly. Most people experience mild symptoms of this from time to time. Sometimes the pharyngotympanic tubes fail to adequately regulate air pressure or allow fluid to drain properly, causing Eustachian tube dysfunction. When you take actions that change the air pressure inside your head, such as swallowing or yawning, muscles in the back of the throat contract, causing the Eustachian tube on each side of your head to open. This is to prevent secretions from the nose from entering the Eustachian tube and contaminating it with fluid and pathogens. The end of the Eustachian tube that connects to the nasopharynx usually remains closed. It could fill up with fluid, providing an environment for bacteria to grow, leading to infection. Without the Eustachian tube, the middle ear would be vulnerable to changes in air pressure caused by ordinary reflexive actions, such as swallowing or yawning.

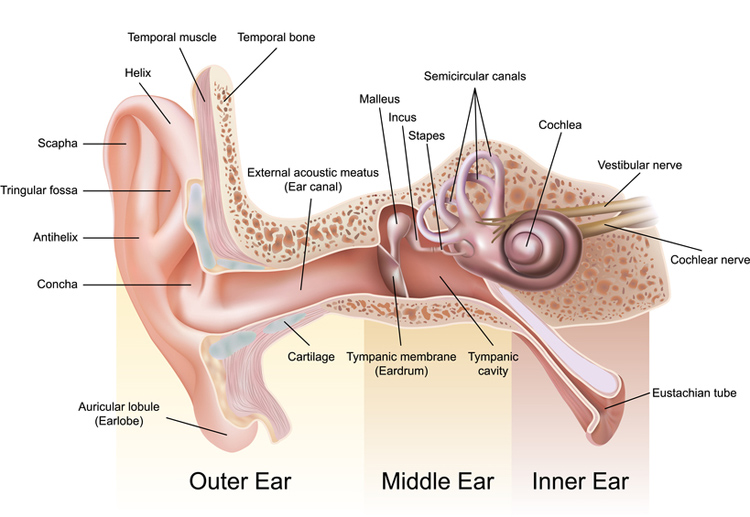
Allow fluid to drain out of the middle ear.The Eustachian tube is a space leading from the middle ear at an angle down into the throat. Certain conditions may cause dysfunction of the tubes that can contribute to hearing loss. You may not be aware of the pharyngotympanic tubes until you experience a problem with them. Pharyngotympanic tubes are more commonly known as Eustachian tubes, deriving this name from Eustachius, an Italian anatomist from the 16th century. The scientific name for these tubes describes where they are found in the body, between the pharynx, or the throat, and the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. The ears are connected to the nasopharynx through the pharyngotympanic tubes. The nasopharynx is the area in the back of the nasal passages that extends down into the throat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
